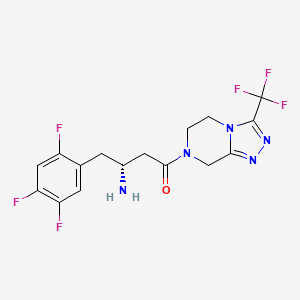

Sitagliptin
Generic Name: Sitagliptin
Brand Names: Januvia
Ingredients: Sitagliptin
Drug Class: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors
Controlled Status: Not a Controlled Substance
Availability: Prescription Medication only
What is Sitagliptin?
Sitagliptin belongs to a class of drugs known as dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. Its mode of action involves enhancing the levels of specific natural substances that work to reduce high blood sugar levels. Sitagliptin is a valuable tool when used in combination with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and occasionally other medications. Its primary purpose is to help adults with type 2 diabetes, a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to the body’s inadequate production or use of insulin.
However, it’s important to note that Sitagliptin is not intended for the treatment of type 1 diabetes, a condition where the body doesn’t produce insulin, leading to an inability to control blood sugar levels.
Sitagliptin is available in various dosage forms, including oral tablets in strengths of 100 mg, 25 mg, and 50 mg. When it comes to its side effects, the commonly experienced ones encompass upper respiratory infections like the common cold or sinus infections, along with symptoms like a runny or stuffy nose and headaches.
Over time, individuals living with diabetes and elevated blood sugar levels may encounter severe or life-threatening complications like heart disease, stroke, kidney issues, nerve damage, and eye problems. Your healthcare team, led by your doctor, will provide guidance on the most effective strategies for managing your diabetes. It’s crucial to engage in open discussions with them to ensure the best outcomes for your health.
What is Sitagliptin Used for?
Sitagliptin is a medication used either alone or in combination with other drugs like insulin, glimepiride, metformin, or pioglitazone, as well as alongside a proper diet and exercise regimen. Its primary purpose is to address elevated blood sugar levels associated with type 2 diabetes. Sitagliptin achieves this by enhancing the release of insulin from the pancreas and signaling the liver to reduce sugar production when blood sugar levels are high. It’s important to note that this medication is not suitable for patients with insulin-dependent or type 1 diabetes. Your doctor’s prescription is essential to obtain Sitagliptin, and it is available in tablet form.
How does Sitagliptin Work?
Sitagliptin operates by competitively inhibiting the activity of an enzyme known as dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4). This enzyme is responsible for breaking down incretins such as GLP-1 and GIP, which are gastrointestinal hormones released in response to food consumption. When Sitagliptin inhibits DPP-4, it prevents the breakdown of GLP-1 and GIP, allowing them to stimulate the release of insulin and suppress the secretion of glucagon by the pancreas’s alpha cells. This action helps bring blood glucose levels closer to the normal range. As blood glucose levels approach normal, the need for insulin release and glucagon suppression decreases, which helps avoid an excessive drop in blood sugar (hypoglycemia), a condition that can occur with certain other oral hypoglycemic agents.
Sitagliptin Dosage
Dosage forms for Sitagliptin are available in tablet form with options of 100 mg, 25 mg, and 50 mg. The recommended typical adult dosage for managing Type 2 diabetes is 100 mg taken orally once daily.
It’s worth noting that when Sitagliptin is used in conjunction with an insulin secretagogue like a sulfonylurea or insulin itself, it may necessitate a lower dosage of the insulin secretagogue or insulin to minimize the risk of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
Sitagliptin is employed as a supplementary treatment to dietary and exercise measures to enhance glycemic control in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus, and the duration of the treatment is determined by the healthcare provider. Additionally, specific dosage adjustments are available for individuals with renal or liver concerns.
For more details about Sitagliptin Dosage
What are the Side Effects of Sitagliptin?
If you experience signs of an allergic reaction such as hives, difficulty in breathing, or swelling in your face or throat, or if you notice severe skin reactions, including symptoms like fever, a sore throat, burning sensation in your eyes, skin pain, or the development of a red or purple rash that spreads and leads to blistering and peeling, seek immediate medical assistance. Additionally, if you encounter symptoms indicative of pancreatitis, like severe upper stomach pain radiating to your back, with or without vomiting, discontinue Sitagliptin and contact your doctor without delay.
It’s essential to be aware that Sitagliptin may give rise to significant side effects. Promptly get in touch with your healthcare provider if you experience a severe autoimmune reaction characterized by itching, blistering, or the breakdown of the outer layer of the skin. Other concerning symptoms include intense and persistent joint pain, diminished or absent urination, or signs of heart failure like breathlessness, even while lying down, swelling in the legs or feet, or rapid weight gain. On a more common note, some less severe side effects of Sitagliptin encompass low blood sugar, headache, or symptoms like a runny or stuffy nose and a sore throat.
For more details about side effects of Sitagliptin
Contact your healthcare provider for guidance regarding any potential side effects. You can also report side effects to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) by calling 1-800-FDA-1088.
How to Use Sitagliptin?
Take this medication orally with a glass of water, following the instructions provided on the prescription label. You have the option to take it with or without food, but do not cut, crush, or chew the medication. To maintain consistency, take your prescribed dose at the same time every day and refrain from taking it more frequently than directed. Do not discontinue usage except upon the advice of your healthcare team. A pharmacist will provide you with a special Med Guide with each prescription and refill; it’s essential to read this information carefully each time.
Discuss the use of this medication in children with your healthcare team, as it is not approved for pediatric use. In the event of a potential overdose, contact a poison control center or seek immediate medical attention. Remember, this medication is intended solely for your use and should not be shared with others.
What Happens if I Miss a Dose of Sitagliptin?
If you forget to take a dose of your medication, take it as soon as you recall. However, if it’s close to the time for your next scheduled dose, it’s best to forgo the missed dose and resume your usual dosing routine. Avoid taking a double dose to compensate for the missed one, as this can lead to potential complications.
What Happens if I Overdose Sitagliptin?
In case of an excessive dose, such as doubling up on your medication or taking it too shortly before your next scheduled dose, there’s an elevated risk of encountering severe side effects, including significant gastrointestinal issues or a potential episode of low blood sugar.
Typical symptoms to be aware of may encompass a rapid heartbeat, trembling, excessive sweating, feelings of nervousness or anxiety, irritability, confusion, dizziness, and heightened sensations of hunger. These signs can often be indicative of specific health conditions or reactions and should not be overlooked.
In case of a medical emergency, please seek immediate medical assistance or contact the Poison Help Line at 1-800-222-1222. Information is also available online at poisonhelp.org. Nevertheless, if you are experiencing severe symptoms, please do not hesitate to dial 911 (or your Local Emergency Number) immediately or proceed to the nearest emergency room for immediate medical attention. Your safety and well-being are paramount.
Pros and Cons of Sitagliptin
| Pros | Cons |
| Once-a-day dosage | Potential for severe joint pain |
| Can be taken with or without food | Not the first choice for individuals with Type 2 diabetes and heart issues |
| No known impact on body weight | May result in sudden kidney injury for those with kidney problems |
Interaction between Sitagliptin and other Drugs
Medications to use with caution
- Abiraterone Acetate
- Acarbose
- Chloroquine
- Chlorothiazide
- Chlorpropamide
- Chlorthalidone
- Ciprofloxacin
- Delafloxacin
- Enoxacin
- Furosemide
- Gatifloxacin
- Gemifloxacin
- Glimepiride
- Glipizide
- Glyburide
- Grepafloxacin
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- Hydroflumethiazide
- Hydroxychloroquine
- Triamterene
- Indapamide
- Lanreotide
- Levofloxacin
- Lomefloxacin
- Metformin
- Metolazone
- Moxifloxacin
- Nateglinide
- Norfloxacin
- Octreotide
- Ofloxacin
- Pasireotide
- Polythiazide
- Repaglinide
- Simeprevir
- Somatrogon-ghla
- Sparfloxacin
- Thioctic Acid
- Tolazamide
- Tolbutamide
Medications that may be prescribed in combination with caution
- Acebutolol
- Atenolol
- Betaxolol
- Bisoprolol
- Carteolol
- Carvedilol
- Celiprolol
- Esmolol
- Labetalol
- Levobunolol
- Metipranolol
- Metoprolol
- Nadolol
- Nebivolol
- Oxprenolol
- Penbutolol
- Pindolol
- Practolol
- Propranolol
- Sotalol
- Timolol
What are the Risks and Warnings for Sitagliptin?
Sitagliptin and Allergy Warning
Please Inform your doctor of any prior unusual or allergic reactions to this medication or other drugs. It’s equally important to inform your healthcare professional about any additional allergies you might have, including those related to foods, dyes, preservatives, or animal allergens. For over-the-counter products, be sure to carefully review the label or packaging for ingredients. Symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as hives, breathing difficulties, or swelling of the face and throat, as well as severe skin reactions, like fever, a sore throat, eye discomfort, skin pain, and the development of a spreading red or purple rash leading to blistering and peeling, should be promptly reported. This comprehensive disclosure is crucial for your healthcare team to ensure your treatment is both safe and effective.
Sitagliptin and Alcohol Warning
The consumption of alcohol can have an impact on blood glucose levels in individuals with diabetes. The extent and frequency of drinking can lead to both hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). It is advisable to refrain from alcohol use if your diabetes is not well managed or if you have conditions like high triglycerides, neuropathy (nerve damage), or pancreatitis. Generally, moderate alcohol intake does not significantly affect blood glucose levels when your diabetes is well controlled. However, it’s important to avoid drinking alcohol on an empty stomach or following exercise, as this can elevate the risk of hypoglycemia.
Sitagliptin and Birth Control Needs
Combining birth control pills with Sitagliptin might reduce the effectiveness of Sitagliptin in managing your condition. The hormones present in birth control pills have the potential to elevate your blood sugar levels. With higher blood sugar levels, Sitagliptin may not function as effectively as it should.
If you are currently using or considering the use of birth control pills while taking Sitagliptin, it’s essential to have a conversation with your doctor. They can provide guidance on the most suitable methods to prevent pregnancy while ensuring your diabetes management remains effective.
Warning with People with Certain Health Conditions
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- A history of gallbladder stones.
- High cholesterol levels in the blood (hypercholesterolemia).
- High triglycerides or fats in the blood (hypertriglyceridemia).
- A history of pancreas problems, which may increase the risk of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
- Pregnant or trying to get pregnant
- Breast-feeding
- A history of angioedema, which is swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat, arms, or legs, particularly related to this medication or other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors.
- Conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis (elevated ketones and acid in the blood) or type 1 diabetes, for which the medication is not suitable.
- A history of heart failure or kidney damage, which may heighten the risk of heart failure.
- Moderate or severe kidney disease, requiring cautious use due to the potential for prolonged medication effects caused by slower elimination from the body.
Warning with other Groups
Sitagliptin and Pregnant Women
Studies in pregnant animals have not indicated any risk to the fetus. However, there is a lack of sufficient research on pregnant women to confirm whether the medication could pose a risk to the unborn child. If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, it’s essential to inform your doctor. The use of Sitagliptin during pregnancy should only be considered if the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks. If you do decide to take this medication during pregnancy, consult with your doctor about participating in the Pregnancy Registry, which monitors the effects of Sitagliptin in pregnant women.
Sitagliptin and Breastfeeding Women
It remains uncertain whether Sitagliptin passes into breast milk or causes any adverse effects in a nursing child. The decision to take Sitagliptin or breastfeed should be made in consultation with your doctor. If your healthcare provider deems it safe for you to use Sitagliptin while breastfeeding, your child should be closely monitored for any potential medication-related side effects.
Sitagliptin and Seniors
As you age, your kidney function may not be as robust as it once was. It’s crucial for your doctor to assess your kidney function before initiating and throughout your treatment with this medication to minimize the risk of side effects.
Sitagliptin and Children
The safety and effectiveness of this drug in children under the age of 18 have not been established.
Images
What are the Alternatives of Sitagliptin?
- linagliptin (Tradjenta)
- metformin (Fortamet, Glumetza)
- empagliflozin (Jardiance)
- canagliflozin (Invokana)
- saxagliptin (Onglyza)
- alogliptin (Nesina)
- glipizide (Glucotrol and Glucotrol XL)
- sitagliptin/metformin (Janumet, Janumet XR)
- pioglitazone (Actos)
- glimepiride (Amaryl)
- liraglutide (Victoza)
- dulaglutide (Trulicity)
- dapagliflozin (Farxiga)
- semaglutide (Ozempic)
FAQs
Sitagliptin phosphate is a medication employed in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is a health condition characterized by insufficient insulin production in the body or the improper functioning of the produced insulin. These factors can result in elevated blood sugar levels, a condition known as hyperglycemia.
Sitagliptin works by elevating the levels of active incretin hormones, leading to increased insulin production and reduced secretion of glucagon from the pancreas’s alpha cells. This combined effect helps to decrease the excessive production of glucose by the liver.
The brand name for sitagliptin is Januvia. Sitagliptin is available as a prescription medication in the form of oral tablets.
Januvia, as indicated in clinical trials, is not associated with either weight gain or weight loss as a side effect. However, it’s important to be aware that a rapid and significant increase in weight could potentially signal more serious side effects related to Januvia. These may include conditions like heart failure or kidney problems. If you experience a sudden and substantial weight gain, it is advisable to promptly contact your doctor for further evaluation and guidance.
Disclaimer
The information provided on this website is intended for general informational purposes only. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Reliance on any information provided here is solely at your own risk. The content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
The website’s content, including text, graphics, images, and other materials, is for informational purposes only.
The website’s content is provided “as is,” and the website owner and authors make no representations or warranties, expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of the information provided. The website owner and authors shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, consequential, or punitive damages arising out of the use of the website’s information.
By using this website, make sure you agree to these terms and conditions.


